1. How does blockchain enhance security in financial transactions?
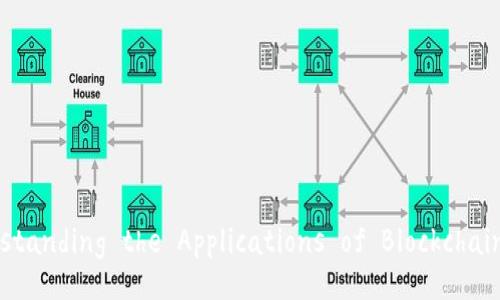
Security is paramount in the financial sector, and blockchain provides a unique solution through its encryption methods and consensus mechanisms. Each transaction is secured via cryptographic hashing, ensuring that only authorized participants can access the data. Additionally, since the data is stored across multiple nodes in a decentralized manner, the risk of hacking is significantly reduced. In traditional banking systems, a single point of failure can expose data to breaches. Conversely, blockchain’s distributed nature ensures that even if one node is compromised, the rest of the network remains intact, providing a robust defense against cyber threats.
Furthermore, the transparency of transactions allows stakeholders to spot fraudulent activities swiftly. As every transaction is recorded and visible to all participants, it becomes challenging to manipulate data without detection. This not only enhances security but also builds trust among users, knowing their financial transactions are safeguarded. In a world increasingly targeted by cybercrime, the security advantages of blockchain are pivotal for financial institutions seeking to protect sensitive customer information.
###2. What challenges does blockchain face in the finance sector?
Despite the numerous benefits of blockchain technology, it is not without challenges. One of the most pressing issues is regulatory uncertainty. Governments worldwide are still grappling with how to regulate blockchain and cryptocurrencies. This lack of clarity can deter financial institutions from adopting the technology, fearing potential legal repercussions.
Scalability is another concern. While blockchain transactions are generally faster than traditional systems, the technology can struggle with a high volume of transactions. Networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum have faced congestion issues during peak usage times, leading to higher transaction fees and slower processing times.
Moreover, integration is a significant challenge for financial institutions already entrenched in traditional systems. Adopting blockchain technology often requires substantial overhauls of existing infrastructure, which can be costly and time-consuming. Lastly, there is also a need for a skilled workforce familiar with blockchain technology. The shortage of qualified professionals can hinder the ability of organizations to implement and maintain blockchain solutions effectively.
###3. How does blockchain impact financial inclusion?
Blockchain technology has the potential to significantly advance financial inclusion, particularly for unbanked populations worldwide. With traditional banking systems often inaccessible in rural or underserved areas, blockchain provides an alternative means of financial transactions. Anyone with a mobile device and internet access can participate in blockchain-based financial services, from payment solutions to lending and investing.
This accessibility breaks down barriers imposing access to financial resources, allowing individuals to store money safely, transfer funds, and even obtain loans without going through traditional banking channels. Moreover, blockchain-based microfinance initiatives can cater to small entrepreneurs who may lack credit history or collateral, granting them the financial assistance needed to grow their businesses.
Additionally, blockchain can drastically reduce the costs associated with cross-border transactions, enabling migrant workers to send money home more affordably. This is particularly important as remittances represent a vital source of income for many families in developing countries. By leveraging blockchain technology, the financial system can become more inclusive, empowering millions who have been historically excluded from the benefits of modern finance.
###4. Can blockchain eliminate fraud in the financial sector?

Blockchain technology holds promise in reducing fraud in the financial sector, primarily due to its inherent security features. The transparency and immutability of blockchain records deter fraudulent activities. Once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted, making fraudulent manipulation nearly impossible. Users can verify transactions at any time and have access to the entire transaction history, reducing the chances of disputes and fraudulent claims.
Furthermore, blockchain can facilitate better identity verification processes, ensuring that participants are who they claim to be. In traditional systems, identity theft is a common problem that leads to significant financial losses. However, with blockchain, individuals can provide a single, verifiable identity that facilitates secure financial interactions without the need for extensive personal information, thus minimizing exposure and risk.
However, it is essential to note that while blockchain significantly reduces fraud, it does not eliminate it entirely. For instance, if a user willingly engages in a fraudulent act, blockchain technology can track the transaction, but it cannot prevent the initial fraudulent intent. Education and vigilance are still necessary components in combating fraud in the financial sector.
###5. How does blockchain influence the future of banking?
Blockchain has the potential to reshape the banking landscape fundamentally. The traditional banking model, characterized by centralization and reliance on intermediaries, may soon become obsolete as blockchain offers a new paradigm of decentralized finance (DeFi). DeFi initiatives aim to create open-source financial applications that provide a range of services without the need for traditional banks.
With the rise of blockchain technology, banks may need to adapt by enhancing their digital offerings and reducing fees to remain competitive. This shift could lead to the emergence of new financial products that were previously not possible or too costly to offer through traditional means. Furthermore, banks may leverage blockchain for internal operations, improving efficiencies in areas like compliance, risk management, and transaction processing.
The focus will likely shift toward building strategic partnerships with fintech companies that specialize in blockchain technology. This collaboration can enable banks to innovate while managing regulatory compliance effectively. As consumers become more accustomed to digital currencies and decentralized banking, the need for banks to provide innovative financial solutions will become increasingly essential for their survival in this evolving landscape.
###6. What is the future potential of blockchain technology in finance?
The future potential of blockchain in finance is immense. As technology evolves, we can expect broader adoption across various financial services. Institutions are already exploring the use of private blockchains to streamline operations and improve security. The development of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) presents a significant opportunity for blockchain to be integrated into national monetary systems, bridging the gap between traditional finance and cryptocurrency.
Moreover, advancements in interoperability could lead to the seamless transfer of assets across different blockchains, enhancing efficiency in financial transactions. Innovations such as Layer 2 solutions aim to improve scalability while maintaining the security of the blockchain, making it more viable for mass adoption.
Investments in research and development will drive further innovations in blockchain applications, resulting in new financial instruments and services. As consumers demand faster, cheaper, and more secure financial transactions, blockchain will likely play a crucial role in meeting these needs.
--- In conclusion, blockchain technology's applications in finance are extensive and varied. It offers unique solutions to long-standing challenges within the industry, from enhancing security and efficiency to promoting financial inclusion. As the technology progresses and matures, we can expect it to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of finance.